Introduction:
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s marketing strategies, objectives, and tactics designed to attract and engage target audiences. It serves as a comprehensive roadmap that guides businesses in aligning their marketing efforts with their overall business goals. By establishing clear marketing strategies, a well-crafted marketing plan helps businesses effectively allocate resources, identify key opportunities, and track progress toward measurable results.
The importance of a marketing plan lies in its ability to provide a structured approach to achieving both short-term and long-term goals. Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, driving sales, or entering new markets, a marketing plan ensures that every marketing initiative is aligned with the business’s objectives. This focused approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and adapt to market changes, ultimately driving sustainable growth and success.
Market Research
Market research is the foundation of any successful marketing plan. Understanding the market landscape—including industry trends, customer needs, and competitive dynamics—provides critical insights that guide the development of effective marketing strategies. Without thorough research, businesses risk missing key opportunities, misreading customer preferences, or failing to identify potential threats.
Industry trends help businesses stay ahead of changes in consumer behavior, technology, and market conditions, allowing them to anticipate shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly. Customer needs and preferences reveal what products and services are most valued, which enables businesses to tailor their offerings to meet these demands. Meanwhile, competitive analysis helps businesses understand how they compare to others in the industry and identify gaps that can be exploited for competitive advantage.
By conducting comprehensive market research, businesses gain valuable data that informs their marketing decisions, from product development and pricing strategies to promotional campaigns and customer engagement tactics. This research-driven approach ensures that the marketing plan is grounded in reality and designed to maximize success.
Define Target Audience
Defining and understanding the target audience is a crucial step in creating an effective marketing plan. The more clearly a business can identify its target audience, the more tailored and relevant its marketing efforts will be. Segmentation based on demographics, behaviors, interests, and pain points helps businesses communicate more effectively with potential customers, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
Demographics, such as age, gender, income level, and education, offer insights into who the audience is. Behavioral factors, like purchasing habits, product preferences, and online activity, reveal how they engage with products or services. Additionally, understanding the specific challenges or pain points that your audience faces allows you to create messaging that speaks directly to their needs, positioning your product or service as the solution.
Effective audience segmentation ensures that businesses can craft targeted messages, choose appropriate marketing channels, and design offers that resonate with the right people at the right time. A well-defined target audience not only enhances marketing effectiveness but also maximizes return on investment (ROI) by focusing efforts on those most likely to convert. By aligning the marketing plan with the audience’s preferences and pain points, businesses can build stronger connections and drive better results.
Set SMART Marketing Objectives
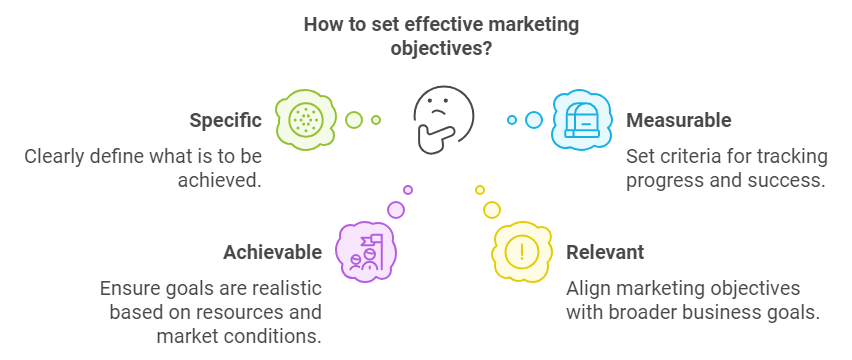
Setting clear and actionable marketing objectives is critical to the success of any marketing plan. The SMART framework—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—is widely used to create goals that provide clarity and direction.
- Specific: Goals should be well-defined and clearly state what is to be achieved. For example, instead of saying “increase sales,” a specific objective would be “increase online sales of product X by 20%.”
- Measurable: Each goal must have criteria for measuring progress and success. This allows businesses to track performance and assess whether objectives are being met. For instance, tracking website traffic, conversion rates, or social media engagement can provide insights into progress.
- Achievable: Goals should be realistic based on available resources and market conditions. Setting overly ambitious targets may demotivate teams or waste resources, while setting achievable goals keeps teams focused and motivated.
- Relevant: Marketing objectives should align with broader business goals. If a company is aiming to expand into new markets, its marketing objectives should focus on brand awareness or lead generation in those regions.
- Time-bound: Each goal should have a clear deadline, creating urgency and accountability. For example, “achieve a 20% increase in online sales within six months” ensures the marketing plan stays on track and provides a timeline for review.
By setting SMART objectives, businesses can align their marketing activities with broader organizational goals, ensuring a focused approach. These well-defined objectives serve as benchmarks for performance, making it easier to evaluate success and adapt strategies as needed.
Craft the Value Proposition
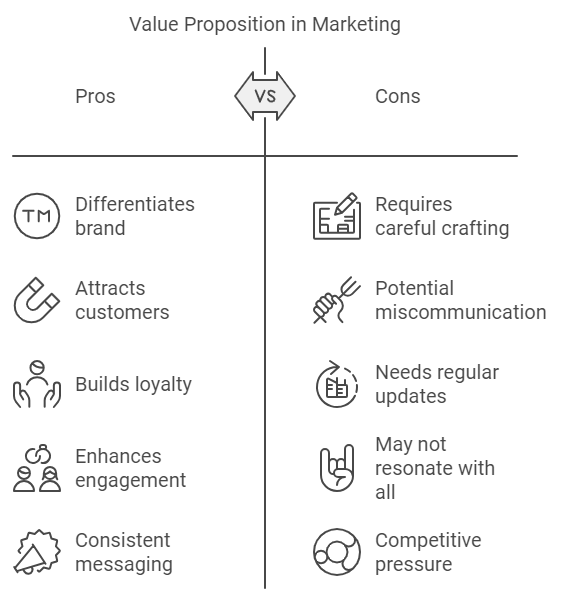
A clear and compelling value proposition is a vital component of any marketing plan. The value proposition succinctly communicates the unique benefits and advantages of a product or service to potential customers. It answers the fundamental question: “Why should customers choose your product over the competition?”
A well-crafted value proposition highlights what makes your offering unique—whether it’s superior quality, innovative features, exceptional customer service, or competitive pricing. For example, a tech company might emphasize cutting-edge features that set its product apart from competitors, while a fashion brand may focus on sustainable materials or ethical production practices.
The value proposition is essential because it serves as the foundation for all marketing messages and positioning. It differentiates your business in the marketplace, helping customers understand why your product or service is the best solution to their problem. A strong value proposition not only attracts potential customers but also builds brand loyalty by clearly communicating the benefits they will receive.
Incorporating the value proposition into your marketing plan ensures consistency across all marketing channels and tactics, reinforcing your brand’s core message and enhancing customer engagement.
Develop the Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
The marketing mix, commonly referred to as the 4 Ps—Product, Price, Place, and Promotion—is a key element in developing a successful marketing plan. Each of these components plays a crucial role in shaping the strategy and ensuring it aligns with business objectives and market demands.
- Product: This involves the goods or services you offer, including their features, design, and quality. Your marketing plan must clearly define how your product satisfies customer needs. Whether you’re launching a new product or promoting an existing one, it’s important to ensure that your product stands out in the marketplace. Product differentiation, including packaging and branding, is essential for creating a strong value proposition.
- Price: Pricing strategy is critical in attracting the right customers while remaining competitive. It must reflect the product’s perceived value, target market, and competitors’ pricing strategies. For example, a premium product may have a higher price point to reflect its exclusivity, while a budget-friendly product might focus on offering the best value for money.
- Place: Place refers to how and where your product is distributed and made available to customers. This could include physical retail locations, e-commerce platforms, or third-party distributors. Ensuring your product is accessible in the right locations based on where your target audience shops is crucial. For instance, if your customers prefer online shopping, investing in strong e-commerce channels is essential.
- Promotion: Promotion encompasses all activities that communicate your product’s value to the target audience. This includes advertising, public relations, digital marketing, social media campaigns, and more. Your promotion strategy should be tailored to the preferences of your audience and aligned with your business goals. For example, if your audience is highly active on social media, prioritizing digital and social media marketing will drive better engagement.
Each element of the 4 Ps must work in harmony to effectively support the marketing plan. By carefully tailoring the product, price, place, and promotion strategies to the market and business objectives, companies can create a cohesive approach that drives sales, boosts customer engagement, and supports long-term growth.
Budget and Resource Allocation
A clear and well-defined budget is crucial to the success of any marketing plan. Allocating resources efficiently ensures that the plan is both effective and sustainable. Without a properly set budget, businesses risk overspending on ineffective tactics or underfunding initiatives that could drive significant results.
The first step in setting a marketing budget is to determine the overall financial commitment the company can afford to allocate for marketing activities. This budget must reflect the company’s goals, market conditions, and available resources. Once the total budget is set, the next step is to allocate resources across various channels and tactics. Prioritizing spending on channels that are proven to drive results for your target audience—such as digital advertising, social media, content marketing, or email marketing—ensures that you get the best return on investment (ROI).
It’s also important to maintain flexibility in the budget, allowing for adjustments based on performance data. For example, if a specific campaign is outperforming others, reallocating resources toward that successful initiative can optimize results. Conversely, if a strategy is underperforming, shifting funds away from it and into more effective channels can help prevent wasted resources.
In summary, an effective marketing budget not only supports the immediate execution of the marketing plan but also ensures long-term sustainability and growth by making the most of available resources.
Measure and Analyze Performance
Measuring and analyzing performance is essential for determining the effectiveness of your marketing plan. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides critical insights into which marketing efforts are working and which may need adjustment. Common KPIs include metrics like website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost (CAC), return on investment (ROI), and social media engagement.
Regularly reviewing performance data allows businesses to assess progress toward marketing objectives and make informed decisions on how to improve outcomes. For example, if your goal is to increase website traffic, monitoring analytics can show which channels are driving the most visitors. If email marketing is performing better than social media, you may decide to allocate more resources to email campaigns.
Continuous optimization based on performance analysis is key to maximizing results. By identifying underperforming areas, businesses can refine their tactics, adjust messaging, or change targeting strategies to improve overall effectiveness. This iterative process helps businesses stay agile and responsive to changing market conditions, ensuring that the marketing plan remains aligned with business objectives and adapts to new opportunities or challenges.
Ultimately, ongoing measurement and analysis not only improve ROI but also create a feedback loop that ensures the marketing plan evolves over time, staying relevant and competitive in a dynamic marketplace.
Conclusion:
A well-crafted marketing plan is a powerful tool that aligns marketing strategies with broader business objectives. By following the seven key components—conducting thorough market research, defining the target audience, setting SMART objectives, crafting a compelling value proposition, developing the marketing mix, allocating the budget efficiently, and continuously measuring and optimizing performance—businesses can create a strategic roadmap for sustainable growth and success.
This approach ensures that every marketing initiative is purposeful, data-driven, and adaptable to changing market conditions. A strong marketing plan not only drives immediate results but also positions the business for long-term competitive advantage, enabling it to thrive in an ever-evolving marketplace.

Juan is a Digital Advertising / SEM Specialist with over 10 years of experience with Google AdWords, Bing Ad Center, Facebook, LinkedIn, Google Analytics, HTML, and WordPress. He is a co-founder of Sheaf Media Group and has work in several online advertising projects for retail, automotive, and service industries. Additionally, Juan holds a bachelor’s degree in Psychology and has a deep interest in the science of human behavior which he attributes as the key factor for his success in the advertising world.


