Marketing Planning Process – A well-structured marketing planning process forms the backbone of successful business growth. Whether you’re launching a startup or managing an established enterprise, understanding how to create and execute an effective marketing plan can make the difference between thriving and merely surviving in today’s competitive marketplace.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every aspect of the marketing planning process, from initial analysis to implementation and monitoring. You’ll discover practical frameworks, real-world examples, and actionable strategies that help transform your marketing efforts from scattered tactics into a cohesive, results-driven approach.
What is Marketing Planning Process
The marketing planning process is a systematic approach to developing, implementing, and evaluating marketing strategies that align with your business objectives. It provides a structured framework for making informed decisions about how to reach your target audience, allocate resources, and measure success.
Definition and Importance
At its core, the marketing planning process involves analyzing your current market position, setting clear objectives, developing strategies to achieve those goals, implementing tactics, and continuously monitoring performance. This methodical approach ensures that every marketing activity serves a specific purpose and contributes to your overall business success.
The importance of following a structured marketing planning process cannot be overstated. Organizations that invest time in comprehensive planning typically experience better resource allocation, improved team alignment, and more predictable results. Without this framework, marketing efforts often become reactive rather than proactive, leading to wasted budgets and missed opportunities.
A well-executed marketing planning process also provides clarity for your entire team. When everyone understands the goals, strategies, and their individual roles in achieving them, collaboration improves and execution becomes more efficient. This alignment is particularly crucial in larger organizations where multiple departments must coordinate their efforts.
Key Components of Effective Marketing Planning
Successful marketing planning encompasses several essential components that work together to create a comprehensive strategy. Understanding these elements helps ensure your planning process addresses all critical aspects of your marketing efforts.
First, market research forms the foundation of effective planning. This includes analyzing industry trends, understanding competitor strategies, and gaining deep insights into customer behaviors and preferences. Without thorough research, your planning efforts lack the necessary context to make informed decisions.
Second, clear objective setting provides direction and measurable targets for your marketing activities. These objectives should be specific, achievable, and directly tied to broader business goals. Whether you’re aiming to increase brand awareness, generate leads, or boost customer retention, well-defined objectives guide every subsequent planning decision.
Third, resource allocation ensures you have the necessary budget, personnel, and tools to execute your plans effectively. This component requires careful consideration of both current capabilities and future needs, helping you identify gaps that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Finally, performance measurement systems enable continuous improvement and accountability. By establishing key performance indicators and regular review processes, you can track progress, identify areas for optimization, and demonstrate the value of your marketing investments.
5 Steps of Marketing Planning Process
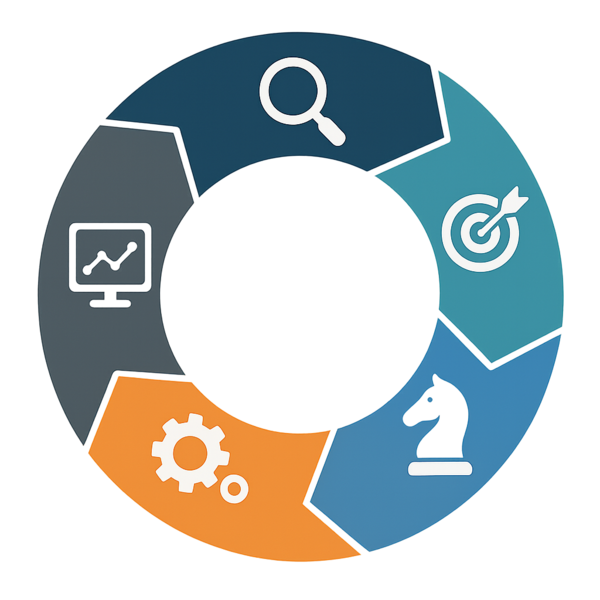
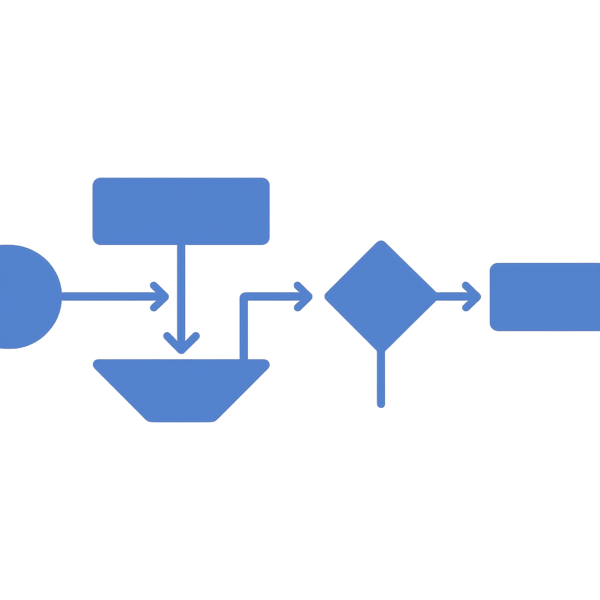
The marketing planning process typically follows five essential steps that build upon each other to create a comprehensive strategy. Each step requires careful attention and thorough execution to ensure your overall plan delivers the desired results.
Step 1: Situation Analysis
The situation analysis phase involves conducting a comprehensive assessment of your current market position, internal capabilities, and external environment. This critical first step provides the insights needed to make informed decisions throughout the rest of the planning process.
Begin by examining your internal strengths and weaknesses. Evaluate your current marketing performance, team capabilities, technological resources, and budget constraints. Consider what unique advantages your organization possesses and where improvements are needed. This honest assessment helps identify areas where you can leverage existing strengths and address limitations that might hinder success.
Next, analyze the external environment to understand opportunities and threats. Study market trends, competitive landscapes, regulatory changes, and technological developments that could impact your business. Pay particular attention to shifts in customer behavior, emerging channels, and evolving industry best practices.
Customer analysis deserves special attention during this phase. Develop detailed buyer personas that capture demographic information, psychographic characteristics, purchasing behaviors, and communication preferences. Understanding your target audience at this level enables more effective strategy development in subsequent steps.
Finally, synthesize your findings into a SWOT analysis that clearly identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This summary document serves as a reference point throughout the planning process, ensuring strategies address key insights from your research.
Step 2: Setting Marketing Objectives
With a clear understanding of your current situation, the next step involves establishing specific marketing objectives that guide your efforts. These objectives should directly support broader business goals while providing measurable targets for your marketing team.
Effective marketing objectives follow the SMART framework: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Rather than setting vague goals like “increase brand awareness,” create precise objectives such as “achieve 25% growth in website traffic from organic search within six months.”
Consider both short-term and long-term objectives to balance immediate needs with sustainable growth. Short-term objectives might focus on quick wins like improving conversion rates or launching a new product campaign. Long-term objectives address broader initiatives such as market expansion or brand positioning changes.
Prioritization plays a crucial role in objective setting. While you may identify numerous desirable outcomes, focusing on a manageable number of high-impact objectives increases the likelihood of success. Consider factors such as resource requirements, potential return on investment, and strategic importance when determining which objectives to pursue.
Document your objectives clearly and share them with all stakeholders. This transparency ensures everyone understands what success looks like and how their contributions support overall goals. Regular communication about objectives also maintains focus and motivation throughout the implementation phase.
Step 3: Developing Marketing Strategy
Strategy development transforms your objectives into actionable plans by determining how you’ll achieve your goals. This step requires creative thinking balanced with practical considerations about resources, capabilities, and market realities.
Start by defining your target market segments and positioning strategy. Based on your situation analysis, identify which customer groups offer the best opportunities for growth. Develop clear value propositions that differentiate your offerings and resonate with each segment’s specific needs and preferences.
Select the most appropriate marketing mix elements for your strategy. Consider how product features, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional tactics work together to deliver value to customers. Each element should reinforce your positioning and contribute to achieving your objectives.
Channel selection requires careful evaluation of where your target audience engages with brands and makes purchasing decisions. Modern marketing strategies often incorporate multiple channels, from traditional media to digital platforms and emerging technologies. Choose channels based on audience preferences, competitive presence, and your ability to create compelling content for each platform.
Develop key messages and creative concepts that communicate your value proposition effectively. These messages should be consistent across all channels while being adapted to suit each platform’s unique characteristics and audience expectations. Strong messaging creates emotional connections with customers and drives desired actions.
Step 4: Implementation Planning
Implementation planning translates strategies into specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities. This detailed planning ensures smooth execution and helps prevent common pitfalls that derail marketing initiatives.
Create a comprehensive marketing calendar that outlines all planned activities, campaigns, and milestones. This calendar should include launch dates, content publication schedules, event timelines, and review periods. A well-structured calendar helps coordinate efforts across teams and ensures consistent market presence.
Assign clear roles and responsibilities for each marketing activity. Document who owns each task, what resources they need, and when deliverables are due. This clarity prevents confusion, reduces duplication of effort, and ensures accountability throughout the implementation process.
Develop detailed budgets that allocate resources across different initiatives and channels. Include both fixed costs like software subscriptions and variable costs like advertising spend. Build in contingency funds to address unexpected opportunities or challenges that arise during implementation.
Establish processes and workflows that support efficient execution. This includes content approval procedures, campaign launch checklists, and collaboration protocols. Well-designed processes reduce errors, speed up execution, and maintain quality standards across all marketing activities.
Step 5: Monitoring and Control
The final step in the marketing planning process involves continuous monitoring of performance and making adjustments based on results. This ongoing evaluation ensures your marketing efforts remain effective and aligned with changing market conditions.
Implement robust tracking systems that capture relevant performance data across all marketing channels. Use analytics tools, customer relationship management systems, and marketing automation platforms to gather comprehensive insights about campaign performance and customer behavior.
Establish regular review cycles to assess progress against objectives. Monthly reviews might focus on tactical performance metrics, while quarterly reviews evaluate strategic progress and market changes. These structured reviews provide opportunities to celebrate successes, identify challenges, and make necessary adjustments.
Create feedback loops that incorporate insights from sales teams, customer service representatives, and customers themselves. This frontline intelligence often reveals opportunities for improvement that aren’t apparent from analytics alone. Regular communication with these stakeholders ensures your marketing remains customer-focused and responsive to market needs.
Document lessons learned and best practices discovered during implementation. This institutional knowledge becomes invaluable for future planning cycles and helps your organization continuously improve its marketing effectiveness. Share these insights broadly to benefit the entire team.
Marketing Planning Process Examples
Real-world examples illustrate how the marketing planning process adapts to different business contexts and objectives. These examples demonstrate the flexibility of the framework while highlighting common elements that drive success across various industries.
B2B Marketing Planning Example
Consider a software company targeting enterprise clients with a new project management solution. Their marketing planning process begins with analyzing the competitive landscape of established players and identifying underserved market segments.
Through situation analysis, they discover that mid-sized companies struggle with the complexity of enterprise solutions but have outgrown basic tools. This insight shapes their objective to capture 15% market share in this segment within two years.
Their strategy focuses on thought leadership content marketing, emphasizing ease of implementation and scalability. They develop case studies, whitepapers, and webinar series that address specific pain points identified during research. The implementation plan includes a phased approach, starting with content creation and SEO optimization before launching paid campaigns.
Monitoring focuses on lead quality metrics, sales cycle length, and customer acquisition costs. Regular analysis of these metrics guides ongoing optimization, such as refining targeting parameters and adjusting messaging based on what resonates most with prospects.
B2C Marketing Planning Example
A retail fashion brand planning to expand its e-commerce presence demonstrates how the process applies to consumer markets. Their situation analysis reveals changing shopping behaviors, with customers expecting seamless omnichannel experiences.
They set objectives to increase online revenue by 40% while maintaining store traffic. Their strategy integrates digital and physical touchpoints, using mobile apps to enhance in-store experiences and social media to drive online sales.
Implementation includes launching a loyalty program that rewards both online and offline purchases, creating shoppable social media content, and training store associates to support omnichannel services. They coordinate inventory management systems to enable features like buy-online-pickup-in-store.
Performance tracking encompasses traditional retail metrics alongside digital engagement indicators. They monitor cart abandonment rates, social media engagement, and cross-channel purchase patterns to optimize the customer journey continuously.
Digital Marketing Planning Example
A startup launching a mobile app for personal finance management showcases digital-first planning approaches. Their situation analysis focuses heavily on app store dynamics, user acquisition costs, and retention benchmarks in the fintech category.
Objectives center on achieving 100,000 active users within the first year while maintaining a customer acquisition cost below lifetime value targets. Their strategy emphasizes content marketing through financial education, influencer partnerships, and app store optimization.
The implementation plan follows a growth hacking methodology, with rapid testing of different acquisition channels and messaging approaches. They allocate resources flexibly, shifting budgets to the highest-performing channels based on real-time data.
Monitoring goes beyond use numbers to focus on user engagement metrics, feature adoption rates, and referral patterns. They implement cohort analysis to understand user behavior over time and identify the most valuable customer segments for targeted retention efforts.
Visual Diagrams and Flowcharts
Visual representations of the marketing planning process help teams understand complex relationships and workflows more easily. Different frameworks offer various perspectives on how to approach planning, each with unique benefits for specific situations.
Traditional 5-Step Process Flow
The traditional five-step marketing planning process follows a linear progression from analysis through implementation. This straightforward approach works well for organizations new to formal planning or those operating in relatively stable markets.
The flow begins with situation analysis, represented as the foundation upon which all other steps build. Arrows indicate how insights from this analysis inform objective setting, which then guides strategy development. Implementation planning translates strategies into specific actions, while monitoring creates a feedback loop back to situation analysis.
This visual representation emphasizes the sequential nature of planning while acknowledging that real-world execution often requires iteration. Teams can use this framework to ensure they complete each step thoroughly before moving forward, reducing the risk of building strategies on incomplete information.
Annotations on the diagram can highlight key deliverables from each step, such as SWOT analysis from situation assessment or KPI dashboards from monitoring activities. These visual cues help teams understand what concrete outputs they should produce at each stage.
Expanded 7-Step Framework
Some organizations benefit from a more detailed seven-step framework that adds preliminary steps for mission alignment and concludes with formal evaluation processes. This expanded approach suits complex organizations or those undertaking significant strategic shifts.
The additional steps typically include an initial phase for reviewing organizational mission and vision, ensuring marketing plans align with broader corporate strategy. A dedicated budgeting step between strategy and implementation provides more detailed financial planning.
The seventh step often involves formal post-campaign analysis and planning cycle reviews. This structured reflection ensures organizations capture learnings and improve their planning processes over time. Visual representations show how these additional steps integrate with the traditional five-step flow.
This expanded framework particularly benefits organizations with multiple stakeholder groups or those requiring extensive approval processes. The additional structure helps manage complexity while maintaining momentum through the planning cycle.
Kotler’s Marketing Planning Model
Philip Kotler’s influential marketing planning model emphasizes the strategic nature of marketing decisions and their connection to corporate strategy. This model provides a more sophisticated view of how marketing planning fits within broader business planning processes.
Kotler’s approach begins with corporate strategic planning, highlighting how marketing objectives must support overall business goals. The model then details marketing strategy formulation, including segmentation, targeting, and positioning decisions that form the core of strategic marketing.
Implementation in Kotler’s model receives significant attention, with explicit consideration of marketing organization, systems, and control mechanisms. This comprehensive view helps organizations understand that successful marketing requires more than good strategies – it demands appropriate structures and processes.
Visual representations of Kotler’s model often use nested diagrams to show how tactical decisions flow from strategic choices. This hierarchical view helps teams understand which decisions should be made at different organizational levels and how they interconnect.
Implementation Tips
Successfully executing a marketing planning process requires more than understanding the steps – it demands practical wisdom about common challenges and proven solutions. These implementation tips help organizations navigate the planning process more effectively.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
One frequent mistake involves rushing through the situation analysis phase due to eagerness to start implementing tactics. This impatience often leads to strategies built on assumptions rather than facts. Allocate sufficient time for thorough research, even if it delays other activities. The insights gained during this phase pay dividends throughout the planning cycle.
Another common pitfall is setting unrealistic objectives that ignore resource constraints or market realities. While ambition drives growth, impossible goals demoralize teams and lead to poor resource allocation. Balance aspiration with achievability by grounding objectives in historical performance data and realistic growth projections.
Many organizations also struggle with implementation due to poor communication and coordination. Marketing plans often fail not because strategies are flawed but because execution breaks down. Prevent this by establishing clear communication protocols, regular check-ins, and shared project management systems that keep everyone aligned.
Finally, avoid the temptation to set and forget your marketing plan. Markets change rapidly, and rigid adherence to outdated plans wastes resources and misses opportunities. Build flexibility into your process, scheduling regular reviews and maintaining the agility to adjust tactics based on performance data and market changes.
Best Practices for Success
Start your planning process by securing genuine buy-in from leadership and key stakeholders. When executives understand and support marketing plans, resources flow more readily and cross-functional cooperation improves. Present planning as an investment in predictable growth rather than an administrative burden.
Involve diverse perspectives throughout the planning process. Include representatives from sales, customer service, product development, and other departments that interact with customers. Their insights enrich your understanding of market dynamics and help create more comprehensive strategies.
Document everything thoroughly but concisely. Marketing planning process artifacts should be detailed enough to guide implementation but not so complex that they discourage use. Create executive summaries for leadership, detailed plans for implementers, and quick reference guides for daily use.
Celebrate wins throughout the implementation process, not just at the end. Recognizing progress maintains team motivation and reinforces the value of following a structured planning approach. Share success stories broadly to build organizational support for marketing initiatives.
Tools and Resources
Modern marketing planning benefits from various technological tools that streamline research, planning, and execution. Customer relationship management platforms provide valuable data about customer behaviors and preferences. Marketing automation systems help execute complex campaigns while maintaining personalization at scale.
Analytics platforms deserve special attention as they enable data-driven decision-making throughout the planning process. From Google Analytics for website performance to specialized tools for social media monitoring, choosing the right analytics stack ensures you can measure what matters most to your objectives.
Project management tools keep implementation on track by providing visibility into task progress, resource allocation, and timeline adherence. Whether using simple solutions like Trello or comprehensive platforms like Asana, select tools that match your team’s size and complexity needs.
Don’t overlook the value of external resources. Industry associations often provide benchmarking data and best practice guides. The Marketing and sales | U.S. Small Business Administration offers free resources particularly valuable for smaller organizations developing their first formal marketing plans.
Templates and frameworks can accelerate your planning process while ensuring comprehensive coverage. However, resist the urge to adopt templates wholesale without customization. Every organization has unique circumstances that require tailored approaches to planning.
The marketing planning process provides a proven framework for transforming marketing from a cost center into a growth engine. By following the structured approach outlined in this guide, organizations of any size can develop effective strategies, allocate resources wisely, and achieve measurable results. Remember that successful planning requires both discipline in following the process and flexibility in adapting to changing circumstances. Start with a solid foundation of research, set clear objectives, develop thoughtful strategies, plan implementation carefully, and monitor results continuously. With these elements in place, your marketing efforts will deliver consistent value to both your customers and your organization.

Juan is a Digital Advertising / SEM Specialist with over 10 years of experience with Google AdWords, Bing Ad Center, Facebook, LinkedIn, Google Analytics, HTML, and WordPress. He is a co-founder of Sheaf Media Group and has work in several online advertising projects for retail, automotive, and service industries. Additionally, Juan holds a bachelor’s degree in Psychology and has a deep interest in the science of human behavior which he attributes as the key factor for his success in the advertising world.